고정 헤더 영역
상세 컨텐츠
본문
지금까지 Redis의 정의에 대해서 배워봣잖아?
그럼 이제 실전에서 좀 써먹어 봐야겠지?
Redis에서 가장 많이 사용되는 기능인 Cache를 사용해보자
일단 Springboot에서 사용하는 방법 으로는 2가지 방법이 있어
1. Repository 패턴을 구현하여 구현체를 이용하여 사용하는 방법
2. Spring Cache Abstraction - Spring cache 방식을 사용하는 방법
각각의 장점이 있는데
- Spring cache 방식을 사용하는 경우
1) 간단한 캐싱 (조회, 수정, 삭제)
2) 메서드 단위 캐싱
3) 코드가 깔끔함
4) 대부분의 경우 충분
- RedisRepository 방식
1) 복잡한 Redis 자료구조 사용 (List, Set,Sorted Set)
2) 조회수, 좋아요 같은 카운터 사용
3) 실시간 랭킹 시스템
4) 세밀한 캐시 제어 필요
실무에서는 보통 둘다 사용하는 경우가 많음
-------------------설정방법--------------------------------------
0. docker-compose.yml
version: "3.8"
services:
postgres:
image: postgres:15-alpine
container_name: demo-postgres
environment:
POSTGRES_DB: test_db
POSTGRES_USER: postgres
POSTGRES_PASSWORD: 비밀번호
ports:
- "5432:5432"
volumes:
- postgres_data:/var/lib/postgresql/data
networks:
- demo-network
healthcheck:
test: ["CMD-SHELL", "pg_isready -U postgres"]
interval: 10s
timeout: 5s
retries: 5
redis:
image: redis:8.4.0-alpine
container_name: redis
command: redis-server --requirepass 비밀번호
ports:
- "6379:6379"
volumes:
- redis_data:/data
networks:
- demo-network
healthcheck:
test: [ "CMD", "redis-cli", "-a", "7487", "ping" ]
interval: 10s
timeout: 5s
retries: 5
app:
build:
context: .
dockerfile: Dockerfile
container_name: demo-app
ports:
- "8080:8080"
environment:
SPRING_DATASOURCE_URL: jdbc:postgresql://postgres:5432/test_db
SPRING_DATASOURCE_USERNAME: postgres
SPRING_DATASOURCE_PASSWORD: 7487
SPRING_DATASOURCE_DRIVER_CLASS_NAME: org.postgresql.Driver
SPRING_JPA_DATABASE: postgresql
SPRING_JPA_HIBERNATE_DDL_AUTO: update
SPRING_REDIS_HOST: redis
SPRING_REDIS_PORT: 6379
SPRING_REDIS_PASSWORD: 비밀번호
depends_on:
postgres:
condition: service_healthy
redis:
condition: service_healthy
networks:
- demo-network
volumes:
postgres_data:
redis_data:
networks:
demo-network:
driver: bridge- services에 redis를 추가하고 depends_on에 redis를 설정한다.
- command: redis-server --requirepass 비밀번호를 설정하지 않으면 생략되긴 하지만 운영에서는 비밀번호를 설정하는것이 좋음
1. application.properties
spring.application.name=demo
# JPA
spring.jpa.database=postgresql
spring.jpa.hibernate.ddl-auto=update
spring.jpa.show-sql=true
spring.jpa.properties.hibernate.jdbc.batch_size=1000
spring.jpa.properties.hibernate.order_updates=true
# Database
spring.datasource.url= jdbc:postgresql://localhost:5432/test_db
spring.datasource.username= postgres
spring.datasource.password= 비밀번호
spring.datasource.driver-class-name=org.postgresql.Driver
# HikariCP
spring.datasource.hikari.maximum-pool-size=10
spring.datasource.hikari.minimum-idle=5
spring.datasource.hikari.connection-timeout=30000
spring.datasource.hikari.idle-timeout=600000
spring.datasource.hikari.max-lifetime=1800000
#redis
spring.data.redis.host=${SPRING_REDIS_HOST:localhost}
spring.data.redis.port=${SPRING_REDIS_PORT:6379}
spring.data.redis.password=${SPRING_REDIS_PASSWORD:비밀번호}
spring.cache.type=redis
spring.cache.redis.time-to-live=600000여기서 SPRING_REDIS_* 이 값들은 docker-compose.yml에서 정의된 값
2. build.gradle
plugins {
id 'java'
id 'org.springframework.boot' version '3.5.7'
id 'io.spring.dependency-management' version '1.1.7'
}
group = 'com.samitech'
version = '0.0.1-SNAPSHOT'
description = 'demo'
java {
toolchain {
languageVersion = JavaLanguageVersion.of(17)
}
}
repositories {
mavenCentral()
}
dependencies {
implementation 'org.springframework.boot:spring-boot-starter-web'
implementation 'org.springframework.boot:spring-boot-starter-data-elasticsearch'
implementation 'org.springframework.boot:spring-boot-starter-data-jpa'
implementation 'org.springframework.boot:spring-boot-starter-data-redis'
implementation 'org.springframework.boot:spring-boot-starter-cache'
implementation 'org.springframework.boot:spring-boot-starter-data-jdbc'
implementation 'org.projectlombok:lombok'
implementation 'com.querydsl:querydsl-jpa:5.0.0:jakarta'
implementation 'org.springframework.boot:spring-boot-starter-batch'
implementation 'org.springframework.boot:spring-boot-starter-data-redis-reactive'
implementation 'org.springframework.boot:spring-boot-starter-validation'
implementation 'com.fasterxml.jackson.datatype:jackson-datatype-jsr310'
testImplementation 'org.springframework.boot:spring-boot-starter-test'
testImplementation 'org.springframework.batch:spring-batch-test'
testImplementation 'io.projectreactor:reactor-test'
runtimeOnly 'org.mariadb.jdbc:mariadb-java-client'
runtimeOnly 'com.oracle.database.jdbc:ojdbc11'
runtimeOnly 'org.postgresql:postgresql'
runtimeOnly 'com.mysql:mysql-connector-j'
testRuntimeOnly 'org.junit.platform:junit-platform-launcher'
compileOnly 'org.projectlombok:lombok'
annotationProcessor 'org.projectlombok:lombok'
annotationProcessor 'com.querydsl:querydsl-apt:5.0.0:jakarta'
annotationProcessor 'jakarta.annotation:jakarta.annotation-api'
annotationProcessor 'jakarta.persistence:jakarta.persistence-api'
}
tasks.named('test') {
useJUnitPlatform()
ignoreFailures = true
}- implementation 'org.springframework.boot:spring-boot-starter-data-redis'
Redis import
- implementation 'org.springframework.boot:spring-boot-starter-cache'
Spring cache Import (어노테이션 쓰려면 이거 impl해야됨)
3. RedisConfig
경로는그냥 config 폴더하나 만들고 그 하위에 넣으면됨
package com.example.demo.config;
import com.fasterxml.jackson.databind.ObjectMapper;
import com.fasterxml.jackson.databind.SerializationFeature;
import com.fasterxml.jackson.datatype.jsr310.JavaTimeModule;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value;
import org.springframework.cache.CacheManager;
import org.springframework.cache.annotation.EnableCaching;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.data.redis.cache.RedisCacheConfiguration;
import org.springframework.data.redis.cache.RedisCacheManager;
import org.springframework.data.redis.connection.RedisConnectionFactory;
import org.springframework.data.redis.connection.RedisStandaloneConfiguration;
import org.springframework.data.redis.connection.lettuce.LettuceConnectionFactory;
import org.springframework.data.redis.core.RedisTemplate;
import org.springframework.data.redis.serializer.GenericJackson2JsonRedisSerializer;
import org.springframework.data.redis.serializer.RedisSerializationContext;
import org.springframework.data.redis.serializer.StringRedisSerializer;
import java.time.Duration;
@Configuration
@EnableCaching
public class RedisConfig {
@Value("${spring.data.redis.host}")
private String redisHost;
@Value("${spring.data.redis.port}")
private int redisPort;
@Value("${spring.datasource.password}")
private String redisPassword;
/**
* Redis와의 연결을 위한 Connection을 생성하고 관리하는 메서드
* Spring Cache와 RedisRepository가 공유하여 사용
*/
@Bean
public RedisConnectionFactory redisConnectionFactory() {
RedisStandaloneConfiguration config = new RedisStandaloneConfiguration();
config.setHostName(redisHost);
config.setPort(redisPort);
config.setPassword(redisPassword);
return new LettuceConnectionFactory(config);
}
/**
* Redis 데이터 처리를 위한 템플릿을 구성하는 메서드.
* RedisRepository에서 사용하기 위한 RedisTemplate
* Spring Cache와는 별도로 동작하며, 복잡한 Redis 연산(List, Set, Sorted Set 등)에 사용
*/
@Bean
public RedisTemplate<String, Object> redisTemplate(RedisConnectionFactory connectionFactory) {
RedisTemplate<String, Object> redisTemplate = new RedisTemplate<>();
// Redis를 연결합니다.
redisTemplate.setConnectionFactory(connectionFactory);
// Key-Value 형태로 직렬화를 수행합니다.
redisTemplate.setKeySerializer(new StringRedisSerializer());
redisTemplate.setValueSerializer(new StringRedisSerializer());
// Hash Key-Value 형태로 직렬화를 수행합니다.
redisTemplate.setHashKeySerializer(new StringRedisSerializer());
redisTemplate.setHashValueSerializer(new StringRedisSerializer());
// 기본적으로 직렬화를 수행합니다.
redisTemplate.setDefaultSerializer(new StringRedisSerializer());
// 초기화
redisTemplate.afterPropertiesSet();
return redisTemplate;
}
/**
* Spring Cache를 위한 CacheManager 설정
* @Cacheable, @CacheEvict 등의 어노테이션에서 사용
*/
@Bean
public CacheManager cacheManager(RedisConnectionFactory connectionFactory) {
// ObjectMapper 설정 - LocalDateTime 처리 추가
ObjectMapper objectMapper = new ObjectMapper();
objectMapper.registerModule(new JavaTimeModule());
objectMapper.disable(SerializationFeature.WRITE_DATES_AS_TIMESTAMPS);
GenericJackson2JsonRedisSerializer serializer =
new GenericJackson2JsonRedisSerializer(objectMapper);
RedisCacheConfiguration defaultConfig = RedisCacheConfiguration.defaultCacheConfig()
.serializeKeysWith(
RedisSerializationContext.SerializationPair.fromSerializer(new StringRedisSerializer())
)
.serializeValuesWith(
RedisSerializationContext.SerializationPair.fromSerializer(serializer)
)
.entryTtl(Duration.ofMinutes(10));
return RedisCacheManager.builder(connectionFactory)
.cacheDefaults(defaultConfig)
.build();
}
}
1) RedisConnectionFactory - redis와의 연결을 위한 connection을 생성하고 관리하는 메서드 (공통)
2) RedisTemplate - RedisRepository에서 사용하기위한 메서드 (spring cache와는 별도)
3) CacheManager - 어노테이션 Cache에서 사용하기위해 필요한 메서드
이제 하위는 Repository 구현을 사용할때 필요한 파일
( 어노테이션을 이용한 cache를 할 것 이라면 하위는 필요없음)
4. RedisRopository
package com.example.demo.redis;
import java.util.Collection;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.Set;
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;
public interface RedisRepository {
// ========== String 연산 ==========
void save(String key, String value);
void save(String key, String value, long timeout, TimeUnit unit);
String get(String key);
void delete(String key);
boolean exists(String key);
// TTL 관련
Long getExpire(String key, TimeUnit unit); // 남은 만료 시간 조회
void setExpire(String key, long timeout, TimeUnit unit); // 만료 시간 설정
// 증감 연산 (조회수, 좋아요 수 등)
Long increment(String key);
Long increment(String key, long delta);
Long decrement(String key);
// ========== Hash 연산 (객체 저장) ==========
void saveHash(String key, String hashKey, String value);
void saveHashAll(String key, Map<String, String> map);
String getHash(String key, String hashKey);
Map<String, String> getHashAll(String key);
void deleteHash(String key, String hashKey);
// ========== List 연산 (최근 조회 목록 등) ==========
void pushToList(String key, String value); // 왼쪽에 추가
void pushToListRight(String key, String value); // 오른쪽에 추가
List<String> getList(String key, long start, long end);
Long getListSize(String key);
// ========== Set 연산 (중복 제거, 태그 등) ==========
void addToSet(String key, String... values);
Set<String> getSet(String key);
boolean isMemberOfSet(String key, String value);
void removeFromSet(String key, String value);
// ========== Sorted Set 연산 (랭킹, 리더보드) ==========
void addToSortedSet(String key, String value, double score);
Set<String> getSortedSet(String key, long start, long end);
Long getRank(String key, String value); // 순위 조회
// ========== 다중 키 연산 ==========
Set<String> getKeys(String pattern); // 패턴으로 키 검색
void deleteMultiple(Collection<String> keys); // 여러 키 삭제
}
5. RedisRepositoryImpl
package com.example.demo.redis.impl;
import com.example.demo.redis.RedisRepository;
import org.springframework.data.redis.core.RedisTemplate;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Repository;
import java.util.*;
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;
import java.util.stream.Collectors;
@Repository
public class RedisRepositoryImpl implements RedisRepository {
private final RedisTemplate<String, Object> redisTemplate;
public RedisRepositoryImpl(RedisTemplate<String, Object> redisTemplate) {
this.redisTemplate = redisTemplate;
}
// ========== String 연산 ==========
@Override
public void save(String key, String value) {
redisTemplate.opsForValue().set(key, value);
}
@Override
public void save(String key, String value, long timeout, TimeUnit unit) {
redisTemplate.opsForValue().set(key, value, timeout, unit);
}
@Override
public String get(String key) {
Object value = redisTemplate.opsForValue().get(key);
return value != null ? value.toString() : null;
}
@Override
public void delete(String key) {
redisTemplate.delete(key);
}
@Override
public boolean exists(String key) {
return Boolean.TRUE.equals(redisTemplate.hasKey(key));
}
// ========== TTL 관련 ==========
@Override
public Long getExpire(String key, TimeUnit unit) {
return redisTemplate.getExpire(key, unit);
}
@Override
public void setExpire(String key, long timeout, TimeUnit unit) {
redisTemplate.expire(key, timeout, unit);
}
// ========== 증감 연산 ==========
@Override
public Long increment(String key) {
return redisTemplate.opsForValue().increment(key);
}
@Override
public Long increment(String key, long delta) {
return redisTemplate.opsForValue().increment(key, delta);
}
@Override
public Long decrement(String key) {
return redisTemplate.opsForValue().decrement(key);
}
// ========== Hash 연산 ==========
@Override
public void saveHash(String key, String hashKey, String value) {
redisTemplate.opsForHash().put(key, hashKey, value);
}
@Override
public void saveHashAll(String key, Map<String, String> map) {
redisTemplate.opsForHash().putAll(key, map);
}
@Override
public String getHash(String key, String hashKey) {
Object value = redisTemplate.opsForHash().get(key, hashKey);
return value != null ? value.toString() : null;
}
@Override
public Map<String, String> getHashAll(String key) {
Map<Object, Object> entries = redisTemplate.opsForHash().entries(key);
return entries.entrySet().stream()
.collect(Collectors.toMap(
e -> e.getKey().toString(),
e -> e.getValue().toString()
));
}
@Override
public void deleteHash(String key, String hashKey) {
redisTemplate.opsForHash().delete(key, hashKey);
}
// ========== List 연산 ==========
@Override
public void pushToList(String key, String value) {
redisTemplate.opsForList().leftPush(key, value);
}
@Override
public void pushToListRight(String key, String value) {
redisTemplate.opsForList().rightPush(key, value);
}
@Override
public List<String> getList(String key, long start, long end) {
List<Object> values = redisTemplate.opsForList().range(key, start, end);
if (values == null) {
return Collections.emptyList();
}
return values.stream()
.map(Object::toString)
.collect(Collectors.toList());
}
@Override
public Long getListSize(String key) {
return redisTemplate.opsForList().size(key);
}
// ========== Set 연산 ==========
@Override
public void addToSet(String key, String... values) {
redisTemplate.opsForSet().add(key, (Object[]) values);
}
@Override
public Set<String> getSet(String key) {
Set<Object> members = redisTemplate.opsForSet().members(key);
if (members == null) {
return Collections.emptySet();
}
return members.stream()
.map(Object::toString)
.collect(Collectors.toSet());
}
@Override
public boolean isMemberOfSet(String key, String value) {
return Boolean.TRUE.equals(redisTemplate.opsForSet().isMember(key, value));
}
@Override
public void removeFromSet(String key, String value) {
redisTemplate.opsForSet().remove(key, value);
}
// ========== Sorted Set 연산 ==========
@Override
public void addToSortedSet(String key, String value, double score) {
redisTemplate.opsForZSet().add(key, value, score);
}
@Override
public Set<String> getSortedSet(String key, long start, long end) {
Set<Object> values = redisTemplate.opsForZSet().range(key, start, end);
if (values == null) {
return Collections.emptySet();
}
return values.stream()
.map(Object::toString)
.collect(Collectors.toSet());
}
@Override
public Long getRank(String key, String value) {
return redisTemplate.opsForZSet().reverseRank(key, value);
}
// ========== 다중 키 연산 ==========
@Override
public Set<String> getKeys(String pattern) {
Set<String> keys = redisTemplate.keys(pattern);
return keys != null ? keys : Collections.emptySet();
}
@Override
public void deleteMultiple(Collection<String> keys) {
redisTemplate.delete(keys);
}
}
------------------------------------------설정 끝---------------------------------------
이제 Cache를 사용해 볼 것인데
나는 귀찮은 관계로 어노테이션을 이용한 작업을 해볼까해
어노테이션으로 메서드 위에 @Cacheable을 한뒤 value, key를 설정하거든 보통
규칙좀 몇개 설명해줄게
=========================================================
value(캐시이름)
// 도메인명 또는 엔티티명을 복수형으로
@Cacheable(value = "products")
@Cacheable(value = "users")
@Cacheable(value = "orders")
// 또는 도메인::기능 형태
@Cacheable(value = "product::list")
@Cacheable(value = "user::profile")
==========================================================
key(캐시키)
// 파라미터 기반
@Cacheable(value = "products", key = "#id")
@Cacheable(value = "users", key = "#userId")
// 복합 키
@Cacheable(value = "products", key = "#category + ':' + #page")
// 전체 조회 시
@Cacheable(value = "products", key = "'all'")
@Cacheable(value = "products", key = "'list'")
// 조건부 전체 조회
@Cacheable(value = "products", key = "'active:' + #isActive")조회 예시
public class ProductService {
// 1. 단순 전체 조회
@Cacheable(value = "products", key = "'all'")
public List<Product> getAllProducts() {
return productRepository.findAll();
}
// 2. 조건부 전체 조회
@Cacheable(value = "products", key = "'category:' + #category")
public List<Product> getProductsByCategory(String category) {
return productRepository.findByCategory(category);
}
// 3. 페이징 전체 조회
@Cacheable(value = "products",
key = "'page:' + #page + ':size:' + #size")
public List<Product> getProducts(int page, int size) {
return productRepository.findAll(
PageRequest.of(page, size)
).getContent();
}
// 4. 단건 조회
@Cacheable(value = "products", key = "#id")
public Product getProduct(Long id) {
return productRepository.findById(id)
.orElseThrow();
}
}
실제로 내가 구현한 메소드에 Cache 사용해보기
package com.example.demo.test.service;
import com.example.demo.test.dao.*;
import com.example.demo.test.vo.ProductDetail;
import com.example.demo.test.vo.ProductDetailWithProductVO;
import com.example.demo.test.vo.RedisTestVO;
import lombok.RequiredArgsConstructor;
import org.springframework.cache.annotation.Cacheable;
import org.springframework.data.domain.PageRequest;
import org.springframework.data.domain.Pageable;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
import org.springframework.transaction.annotation.Transactional;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Map;
@Service
@RequiredArgsConstructor
public class RedisTestService {
private final RedisTestRepository redisTestRepository;
private final ProductDetailReopository productDetailReopository;
private final QueryDslTestRepository queryDslTestRepository;
private final QueryDslDetailRepository queryDslDetailRepository;
private final QueryDslTestDetailInterface queryDslTestDetailInterface;
public List<RedisTestVO> getAllProducts(){
return redisTestRepository.findAllBy();
}
public RedisTestVO getProductData(Long cd){
return redisTestRepository.findByProductCd(cd);
}
public List<RedisTestVO> getTop100Products(){
Pageable pageable = PageRequest.of(0,100);
return redisTestRepository.findAllBy(pageable);
}
@Transactional
public int insertBatchProductsWithDetails(RedisTestVO baseVo, List<ProductDetail> detailInfos) {
// detailInfos: 각 product마다 생성할 detail의 설명 목록 (예: ["상세1", "상세2", ...])
List<RedisTestVO> productList = new ArrayList<>();
for (int i = 1; i <= 10000; i++) {
RedisTestVO product = new RedisTestVO();
product.setProductNm(baseVo.getProductNm() + "_" + i);
product.setPrice(baseVo.getPrice());
product.setCategory(baseVo.getCategory());
product.setDescription(baseVo.getDescription());
// 자식(detail) 생성
List<ProductDetail> details = new ArrayList<>();
for (ProductDetail info : detailInfos) {
ProductDetail detail = new ProductDetail();
detail.setDetailInfo(info.getDetailInfo());
detail.setExtraInfo(info.getExtraInfo());
detail.setProduct(product);
details.add(detail);
}
// 양방향 관계라면 부모의 컬렉션에도 추가
product.setDetails(details);
productList.add(product);
// 배치 단위마다 저장 + flush + clear 전략
if (i % 1000 == 0) {
// saveAll 할 때 cascade로 자식도 같이 저장됨
redisTestRepository.saveAll(productList);
productList.clear();
}
}
// 남은 것 처리
if (!productList.isEmpty()) {
redisTestRepository.saveAll(productList);
redisTestRepository.flush();
}
return 1;
}
public List<RedisTestVO> selectAllProducts(){
return queryDslTestRepository.findAllBy();
}
@Cacheable(value = "productDetails", key = "'all'")
public List<Map<String, Object>> selectAllProductDetail(){
return queryDslTestDetailInterface.selectTest();
}
}젤 하위의 selectAllProductDetail만 보면 될것같다
이제 이 메서드를 실행할때 처음에는 cache miss가 발생하여 db에서 조회를 하겠지만 두번째 부터는
spring AOP Proxy가 가로채서
redis에서 "productDetails::all"를 조회하고
캐시가 있으면 Redis의 값을 반환하게 되어 캐싱 처리가 완료된다
결과
첫번째 조회시
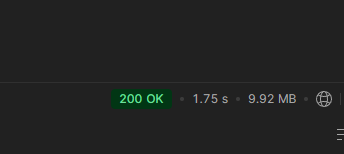
캐싱이 적용된 이후

빨라졋지 확연하게?
이렇게 사용하면 spring boot - redis 연동 끝!
'기술공부 > Redis' 카테고리의 다른 글
| Redis 캐싱에서 DB와의 원자성을 확보하는 법 (0) | 2025.12.01 |
|---|---|
| Redis 캐시 저장방식, 제거방식 (0) | 2025.12.01 |
| Redis 활용 (0) | 2025.11.28 |
| Redis란 (0) | 2025.11.28 |




